Photovoltaics: The basics you should know
Chapter in this post:
- 1 The basics
- 2 History of photovoltaics
- 3 Functionality of solar cells
- 4 advantages and disadvantages of photovoltaics
- 5 accessories and tools from the photovoltaic sector
- 6 topics on the topic
- 7 devices that work with solar
- 8 products that work with solar
- 9 types of solar cells
- 10 monocrystalline solar cells
- 11 polycrystalline solar cells
- 12 thin film solar cells
- 13 Organic solar cells
- 14 components of a photovoltaic system
- 15 solar panels
- 16 inverters
- 17 mounting systems
- 18 solar storage tanks
- 19 charge controllers
- 20 surge protection
- 21 Economic efficiency and profitability of a photovoltaic system
- 22 Acquisition costs
- 23 Feed-in tariff
- 24 own consumption
- 25 payback period
- 26 Increase in the value of the property
- 27 environmental factor
- 28 Future perspectives of solar technology
- 29 Increased efficiency
- 30 Flexibility and integration
- 31 Combination with other technologies
- 32 Sustainable production
- 33 New business models
- 34 Safety aspects and environmental impacts of photovoltaic systems
- 35 Safety during installation and operation
- 36 Environmental Impacts
- 37 Positive environmental impact
- 38 tips for those interested in a photovoltaic system
- 39 Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about photovoltaics
- 40 How long does a photovoltaic system last?
- 41 Can I feed the excess electricity into the grid?
- 42 Do I have to insure my system?
- 43 What happens in the event of a power failure?
- 44 How much electricity can I produce with my system?
- 45 My tips & tricks about technology & Apple
The basics
The sun – an inexhaustible source of energy that has determined our lives for thousands of years. But how can we use this energy directly? This is exactly what photovoltaics is all about.
History of photovoltaics
The idea of converting sunlight into electrical energy is not new. The first experiments with solar cells took place as early as the 19th century. But the real breakthrough came in the 1950s, when space travel discovered the technology. Since then, photovoltaics has come an impressive way. From the first small systems on satellites to huge solar parks that can supply entire cities with electricity.

How solar cells work
At first glance it may seem like magic: a flat panel that converts sunlight into electricity. But there is a fascinating science behind it. When sunlight hits a solar cell, electrons are set in motion by the photovoltaic effect. This movement creates an electric current. Depending on the type and quality of the solar cell, a large part of the incident sunlight can be converted into electricity.
Advantages and disadvantages of photovoltaics
The benefits of photovoltaics are obvious: it provides clean, renewable energy that helps us combat climate change and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. In addition, the operating costs of a solar system after installation are very low.
But there are also challenges: the sun doesn't always shine and energy production can vary. In addition, solar systems require a large area and the production of the modules can be environmentally harmful. Nevertheless, the advantages are compelling and the technology is constantly evolving.

Accessories and tools from the photovoltaic sector
If you want to install a photovoltaic system in your home, you will definitely need a lot of tools and materials - especially when it comes to systems that also integrate a solar storage system. Here is a list of relevant terms
- MC4 connector
- MC4 crimping pliers
- Loosen/open MC4 connector
- MC4 crimping tool Knipex
- MC4 extension cable 10m, 5m, 2m
- MC4 connector plus and minus
- MC4 cable
- MC4 Y connector
- MC4 Evo2
- MC4 window bushing
- MC4 tool
- MC4 on XT60
- MC4 Y connector set for parallel connection of 2 solar modules
- MC4 socket
- MC4 blind plug/end cap
Topics related to the topic
- What is the difference between solar and photovoltaic?
- Advantages and disadvantages of monocrystalline versus polycrystalline solar cells
- How solar trackers increase the efficiency of photovoltaic systems
- Thin-film solar cells: future of solar technology?
- Grid-connected systems vs. stand-alone systems: Which is right for me?
- The role of storage technologies in the solar industry
- Solar farms: How they work and why they are important
Devices that work with solar
- solar fairy lights
- Solar fountain
- Solar balcony power plant
- Solar garden shower
- Solar garden light
- solar charge controller
- Garden fountain solar
- Solar panel for the balcony
- Solar carport
- Solar patio roof
- Solar island system
- Solar table lamp
- Solar lanterns
- solar lantern
- Solar irrigation system/irrigation system
- Garden lighting with solar
- Pond pump with solar
- Solar power station
- Solar outdoor light
- Solar fountain
- Solar house number
- Solar Christmas lights
- Solar panel for camping
- Solar water feature
- Solar hanging light
- Solar socket
- Solar charger cell phone
- Solar outdoor light with motion detector
- House number illuminated solar
- Solar outdoor fairy lights
- Solar lantern outdoor
- Solar lamps garden
- Solar table lamp outdoor
- Solar radio
- solar water pump
Products that work with solar
- Zendure Solar Flow
- Garmin Instinct Solar
- Trina Solar Vertex S
- Fenix 7 Solar
- Garmin Edge 1040 Solar
Types of solar cells
Solar cells come in different shapes and sizes, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's take a closer look.
Monocrystalline solar cells
These solar cells are the "classics" among photovoltaic technologies. They consist of a single, large silicon crystal, which gives them their characteristic dark blue to black color. Due to their high purity, they achieve a high degree of efficiency, which means that they can convert a large part of the incident sunlight into electricity. However, they are also somewhat more expensive to produce.
Polycrystalline solar cells
In contrast to monocrystalline cells, polycrystalline solar cells consist of many small silicon crystals. This gives them a bluish, grainy appearance. They are cheaper to produce, but have a slightly lower efficiency. However, for many applications, especially in areas with less intense solar radiation, they are a good choice.
Thin film solar cells
Thin film technology is a different approach to photovoltaics. Instead of thick silicon wafers, thin layers of materials such as cadmium telluride or copper-indium-gallium-diselenide are applied to a substrate. This makes them flexible and light, but also less efficient than crystalline cells. However, their big advantage is that they work well even in diffuse light, such as on cloudy days.
Organic solar cells
This is really a thing of the future! Organic solar cells are made from carbon-based materials similar to those found in plastic. They are flexible, lightweight and could even be transparent in the future. At present, they are still less efficient and less durable than other cell types, but the research is promising. Maybe in a few years we will be able to use our windows as solar cells!

Components of a photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system does not only consist of solar cells. There are many different components that work together to convert sunlight into usable electricity. Let's take a look at the most important parts.
Solar Panels
This is probably what most people think of first when they hear about photovoltaics. Solar modules are groups of solar cells that are grouped together and mounted in a frame. They capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy.
Inverters for Home
After the solar panels have generated the electricity, the inverter comes into play. It converts the direct current that the modules produce into alternating current that we can use in our homes and businesses.

mounting systems
In order for the solar modules to be mounted safely and efficiently, you need a good mounting system. There are various systems for roofs, open spaces or even for mounting on facades.
Solar storage
We don't always use electricity exactly when the sun is shining. This is where solar storage comes into play. They store excess energy produced on sunny days so we can use it at night or on cloudy days.
charge controller
If you have a solar storage tank, you also need a charge controller. It ensures that the memory is charged correctly and protects it from overcharging or deep discharge.
overvoltage protection
As with any electrical system, it is important to protect yourself from power surges that can be caused by lightning or other disturbances. A good surge protector can keep your system and your home safe.

Economic efficiency and profitability of a photovoltaic system
Installing a photovoltaic system is not only a contribution to environmental protection, but can also make economic sense. But how profitable is such an investment really?
acquisition cost
The first thing to consider is of course the cost. These can vary depending on the size of the system, type of solar cells and other factors. In recent years, however, the prices for solar technology have fallen significantly, which makes the purchase more attractive.
feed
In many countries there is a feed-in tariff for the electricity you feed into the grid. This means that you receive compensation for every kilowatt hour that you produce and do not consume yourself. This can be an important factor in the profitability of your investment.
ownconsumption
The more electricity you use yourself, the less dependent you are on rising electricity prices. With good energy management and possibly a solar storage system, you can maximize your self-consumption and minimize your electricity bill.
Payback period
The payback period indicates how long it takes until you have recouped the purchase costs through the saved electricity costs and the feed-in tariff. Depending on the system and general conditions, this time can be between 8 and 15 years.
increase in value of the property
A photovoltaic system can also increase the value of your property. More and more buyers value energy-efficient homes, and a solar system can be an attractive selling point.
environmental factor
In addition to the purely economic aspects, one should not ignore the environmental factor. With a photovoltaic system you reduce your CO2 footprint and make a contribution to climate protection.

Future prospects for solar technology
Photovoltaics have made enormous progress in the last few decades. But what does the future bring? Here is a look at the exciting developments and trends in solar technology.
increase in efficiency
Although modern solar cells already achieve impressive levels of efficiency, there is still room for improvement. Researchers are constantly working on new materials and technologies to further increase efficiency. In the coming years, we could see solar cells that can convert even more sunlight into electricity.
Flexibility and integration
The future of solar technology does not only lie in large solar parks or roof systems. Flexible solar cells could be integrated into windows, facades or even clothing. This would make it possible to use almost any surface to generate energy.
Combination with other technologies
Combining photovoltaics with other renewable energy technologies, such as wind power or hydropower, could make energy supplies even more reliable. Smart grids combining different energy sources could be the answer to fluctuating energy production.
sustainable production
The production of solar cells and modules also has an ecological footprint. Future developments could focus on more sustainable production methods that use fewer resources and produce less waste.
New business models
As technology advances, new business models could emerge. Instead of buying solar panels, people could rent them or buy electricity directly from local producers.
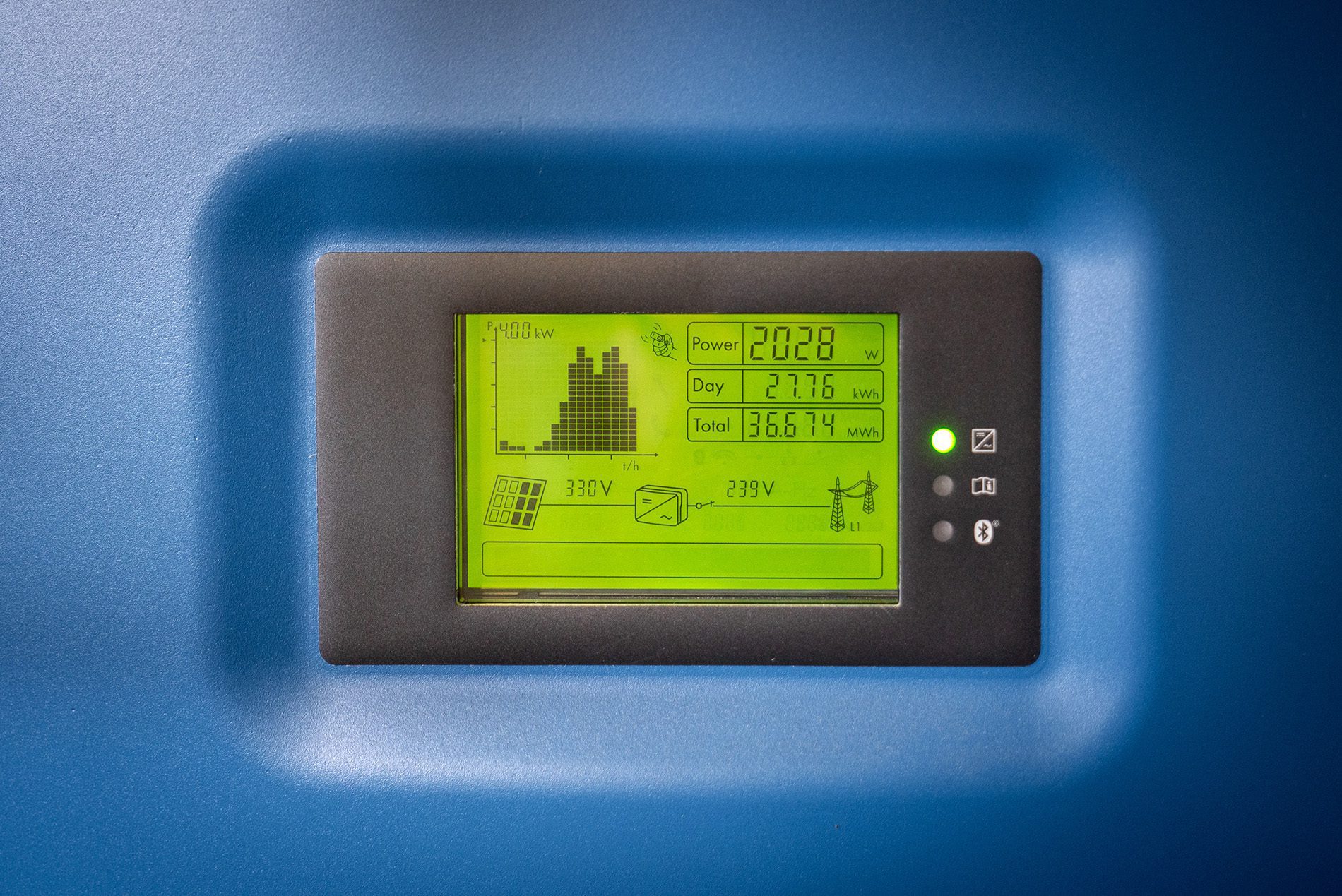

Safety aspects and environmental impacts of photovoltaic systems
While photovoltaic systems offer many benefits, there are also some safety and environmental issues that should be considered. Here is an overview of the most important points.
Safety during installation and operation
- electric security: As with any electrical system, there is a risk of electric shock with solar systems. It is important during installation and maintenance to ensure that all components are properly grounded and that there are no exposed wires.
- Fire protection: There are rare cases where photovoltaic systems have caused fires, mostly due to installation errors or defective components. It is important to regularly inspect the facility and ensure that it conforms to fire safety regulations.
Environmental impact
- resource consumption: The production of solar cells requires the use of materials and energy. It is important to promote sustainable production methods and improve the recycling process.
- waste: At the end of their useful life, solar cells must be disposed of. Since they contain materials such as silicon, metals and sometimes rare earths, it is important to develop effective recycling methods.
- Land use: Large solar parks require a lot of land. It is important to carefully consider the environmental impact of such projects and ensure that they do not result in habitat loss or other ecological problems.
Positive environmental impact
- Reduction of greenhouse gases: Photovoltaic systems produce clean electricity without CO2 emissions. This helps in the fight against climate change.
- Independence from fossil fuels: Solar power reduces dependence on oil, coal and gas, which is not only good for the environment but also for the economy and national security.
Tips for those interested in a photovoltaic system
If you are thinking about installing a photovoltaic system, there are a few things you should consider. Here are some tips to ensure you make the right decision and get the most out of your investment.
- Inform yourself thoroughly: Before you make a decision, it is important to learn as much as possible about photovoltaics. This includes not only the technology itself, but also the economic aspects, funding opportunities and legal framework in your country or federal state.
- Get multiple offers: There are many providers of photovoltaic systems and the prices and services can vary. It is worth obtaining several offers and comparing them carefully.
- Pay attention to quality: Cheap isn't always better. When choosing your system, pay attention to quality and durability. Branded products and certificates can be helpful clues.
- Consider whether you want to save: With a solar storage system you can store the electricity you produce yourself and then use it when the sun is not shining. This increases your own consumption and can make economic sense.
- Plan for the future: Your energy needs may change over time, for example if you buy an electric car. Consider whether you might need more electricity in the future and plan your system accordingly.
- Uses government grants: There are government support programs for photovoltaics in many countries. Find out about this and use these options to reduce costs.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about photovoltaics
There are many questions about the topic of photovoltaics. Here are some of the most common questions and their answers.
How long does a photovoltaic system last?
Most photovoltaic systems are designed for a service life of 20 to 25 years. However, that doesn't mean they won't work afterwards. However, there may be a slight decrease in performance over time.
Can I feed the excess electricity into the grid?
In most countries you can feed the electricity that you do not use yourself into the grid and receive compensation for it. However, the exact regulations and tariffs vary.
Do I have to insure my system?
It is a good idea to insure your photovoltaic system against damage caused by storms, hail or fire, for example. Many insurance companies offer special photovoltaic policies.
What happens in the event of a power failure?
Most photovoltaic systems are designed in such a way that they are automatically disconnected from the grid in the event of a power failure. This is necessary for security reasons. If you want electricity even in the event of a power failure, you need a solar storage system and a special controller.
How much electricity can I produce with my system?
This depends on many factors, such as the size and orientation of the facility, the location and the weather conditions. A professional can give you an accurate estimate.